The rotary vane compressors are used for compression of hydrocarbon and biogas in the processing industry. The rotary vane compressors are simple in design and maintenance-friendly. The distinctive peculiarity of this type of compressor is its turnaround interval amounting to about 100 000.00 hours.

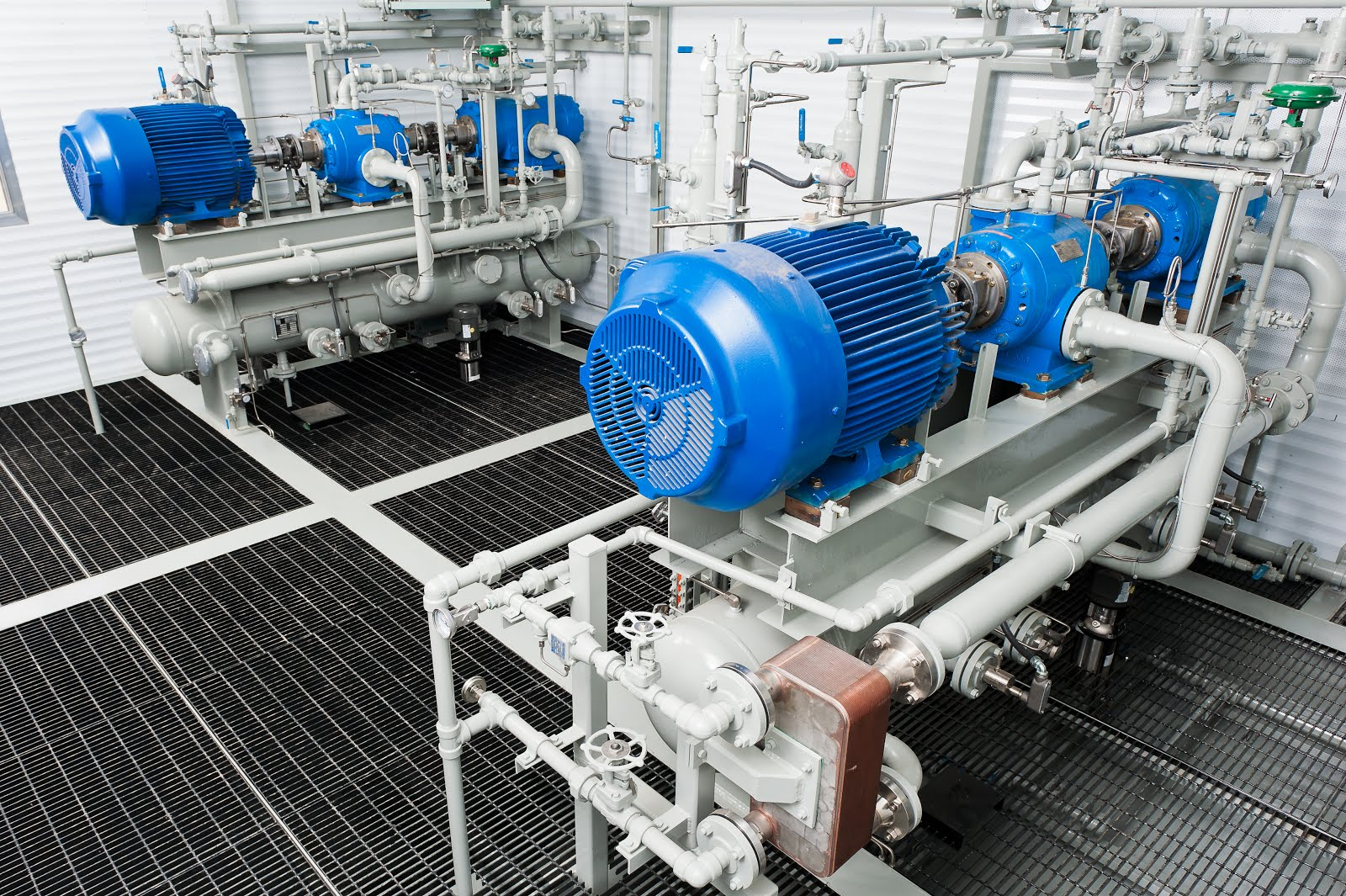
The rotary vane compressors are related to the positive displacement type of machine. The principle of operation of this compressor is as follows. The compressor’s casing is made in the form of a cylinder. Inside the casing is the shaft which is provided with grooves to which plates are movably fixed. The shaft is non-coaxial with the casing. When the rotor turns, the plates touch the walls of the casing and form different-volume chambers. As the shaft rotates, gas gets through the suction nozzle into the compression chamber of the compressor and then, as the rotor turns, travels to the discharge nozzle. During rotation the volume of the compression chambers is constantly decreased, as a result of which gas compression takes place.
The rotary vane compressor’s throughput can be controlled by a bypass line, changing rotational speed of the compressor’s shaft and gas throttling at suction.
The drive unit of a rotary vane compressor may be composed of an electric motor or gasoline, diesel or gas engine. In each particular case, the selection of the type of drive is based on the compressor’s power requirement and availability of fuel reserves or electricity necessary to ensure its operation.
The rotary vane compressor is capable of flowing up to 3500 actual cubic meters per hour of compressed gas (in terms of suction) at pressures of up to 1.0 MPa (abs.) at discharge.
